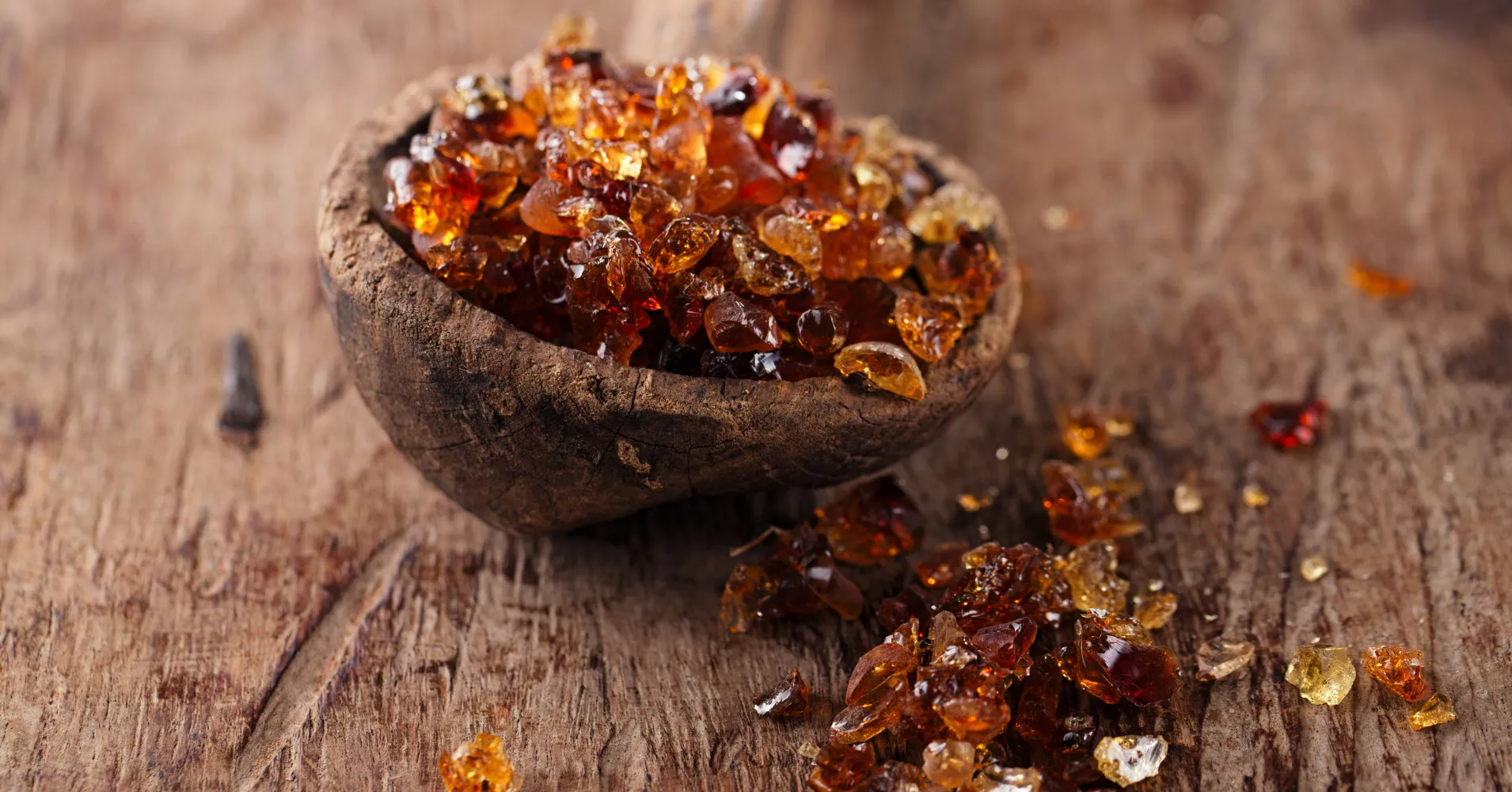
A number of sweets and snacks are really united by one inconspicuous ingredient. On the labels of many foods, it is hidden behind the term E414, but otherwise it is also known as gum arabic. It is most commonly found in Africa’s Sahel zone, and the best quality is harvested in the African Sudan, where an intense military conflict is currently raging. Because of this instability, many gum arabic processors have several months’ supply. But suppliers have warned they do not know when or how supplies of this key raw material will resume. A large amount of Arabic gum passes through the ports of Sudan, and they are now, in view of the situation in the country, suspending its supply. They inform Reuters Which Bild.
Coca-Cola, chewing gum, jelly products, cosmetics, water coloring, medicinal dragees, all these products are united by gum arabic. Gum arabic is the sap obtained from the acacia tree that grows in the Sahel region. There is the so-called “rubber belt” from east to west, where acacia trees grow on the edge of the desert and produce sap from which gum arabic is refined. Estimates vary, but Sudan alone is responsible for around 70-80% of the world’s production of these food binders and stabilizers.
Most of the companies that use gum arabic in their products build stocks around 3 to 6 months due to the instability of the region. While in previous years the main problem was supply in the Darfur region, the economic shutdown in Khartoum, where most of Arba’s rubber is exported to the world, could be far worse.
“Due to the conflict, our suppliers are having difficulty even providing basic necessities. Neither buyers nor sellers know when supplies will stabilize,” said Jinesh Doshi, director of one of the main gum arabic suppliers in India, Vijay Bros. Reuters spoke to 12 major importers of gum arabic from around the world, and all said imports from Sudan had nearly stopped.
“Companies like Pepsi and Coca-Cola couldn’t exist without gum arabic in their recipe,” explains Dani Haddad, director of marketing and development at Agrigum, which is one of the world’s top ten suppliers and is currently based in the UK, but sources most of its production is only in Sudan. For example, the ingredients in Coca-Cola would not last long without gum arabic, and the dyes would leave significant marks on the packaging. However, gum arabic is used, for example, in cosmetics for skin masks and hairsprays, as well as for stamp adhesives.
About 120,000 tonnes of gum arabic are produced annually, mostly in African countries such as Ethiopia, Senegal or Sudan. This brings Sudan alone about $1.1 billion a year. The United States became convinced of the importance of gum arabic since 1997. At that time, it imposed a trade embargo on Sudan, from which, shortly after its introduction, following pressure from Coca-Cola, it was gum arabic. which has been deleted.

“Tv nerd. Passionate food specialist. Travel practitioner. Web guru. Hardcore zombieaholic. Unapologetic music fanatic.”